Zoom In: Trading Fundamentals – Inflation and How to Trade It
If you’re looking to trade news events, you’ve got to understand them first. No stress - that’s exactly why we’re kicking off this fresh article series! In our first piece, we’ll explore how to decode inflation data and turn it to your advantage.

At Fintokei, we’re one of the few prop firms that let you trade during news releases with zero restrictions. Why not make the most of it? That said, if you’re just starting out, you’re probably sticking to chart patterns – and that’s perfectly fine!
But here’s the thing: every aspiring pro trader knows growth is the name of the game. That’s where our Zoomed In on Fundamentals series comes in. It’s your ultimate guide to the economic calendar – helping you understand regular reports, interpret them like a pro, and trade the right instruments at the right time.
In this pilot piece, we’ll break down what inflation means for traders, the types of inflation, the assets to watch, and how markets typically react to inflation reports.
Ready to zoom in and level up? Let’s go! 🌟
Why Is Inflation Important for Traders?
Inflation measures the rise in the overall price level of goods and services in an economy. When inflation increases, it reduces the purchasing power of money. In simple terms, rising inflation means you can buy less for the same amount of money. A moderate level of inflation is natural and even desirable, but high inflation can be destructive to the economy.
Inflation can also turn negative – a phenomenon known as deflation. However, deflation is equally problematic, and central banks do everything they can to avoid it.
For traders, inflation is a game-changer because it directly impacts central bank policies. When inflation exceeds the target level (e.g., 2% for the Fed or ECB), central banks often respond by raising interest rates. This can strengthen the local currency while weakening the stock market. On the flip side, when inflation slows, central banks may cut rates, which supports economic growth and boosts stocks.
CPI, PCE, Core, and Headline Inflation – Who Can Keep Up?
Not all inflation is created equal. To make things more “fun”, economists have broken it down into several types. Let’s clarify them:
- CPI (Consumer Price Index): The CPI measures the changes in prices of everyday goods and services that households typically buy (milk, eggs, butter, fruits, veggies – you know the drill ). Compared to PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures), CPI often reports higher inflation because it doesn’t account for consumers switching to cheaper alternatives. CPI is the go-to measure of inflation worldwide.
- Preliminary CPI: Think of this as CPI’s warm-up act. It’s essentially an early estimate of the CPI, published toward the end of the month, while the standard CPI follows a few weeks later. Although they rarely differ, markets often react more strongly to the preliminary CPI – especially for EUR-linked currencies. So, traders, stay sharp!
- PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures): This one’s a bit of an American favorite – and the Fed’s darling. PCE is less volatile than CPI because it better captures shifts in consumer behavior. For example, if beef prices rise and people start buying cheaper chicken, PCE adjusts for this (unlike CPI). It’s published alongside GDP data, making it a key metric for economic projections.
- Headline vs. Core Inflation: Headline inflation includes everything, even the volatile prices of energy and food. Core inflation, on the other hand, excludes these categories, offering a clearer view of long-term trends. Central banks focus more on core inflation when shaping monetary policy.
What to Trade During Inflation Data Releases
U.S. Dollar (USD): This one’s straightforward: higher-than-expected inflation usually means a stronger dollar. Why? Inflation impacts the Fed’s monetary policy. Higher inflation increases the likelihood of rate hikes, and higher rates strengthen the dollar. On the flip side, lower inflation can weaken it.
Gold (XAU/USD): You probably know that gold tends to move inversely to the dollar. High inflation can boost gold as a hedge against currency devaluation. However, if the central bank starts aggressively hiking rates, gold may take a hit due to rising bond yields. It’s a tricky balance! Check out our guide on the key instruments and indices to watch when trading gold.
Stock Indices (S&P 500, Nasdaq, Dow Jones): Stocks can have mixed reactions to inflation. Mild inflation signals economic growth, which is good for equities. But if inflation gets out of hand and the central bank tightens monetary policy aggressively, stocks often face sharp declines.
Bond Yields (US10Y, US02Y): Higher inflation raises expectations for rate hikes, pushing bond yields higher. For example, a sharp rise in 10-year U.S. Treasury yields often negatively impacts the stock market.
How to Trade Inflation Data
Pre-Release Prep
- Keep an eye on analyst expectations (platforms like Investing.com are a great resource).
- Review how the markets reacted to previous inflation data.
- Assess the current market sentiment – identifying trends can give you an edge.
Post-Release Reactions
- If inflation exceeds expectations, the domestic currency usually strengthens, while stocks may dip.
- If inflation falls below expectations, stocks might rally, while the currency could weaken.
Risk Management
Inflation data often triggers extreme volatility. A stop-loss is your best friend here. Always wait for the market to confirm its direction before jumping into a trade.
How to Trade Inflation – A Practical Example
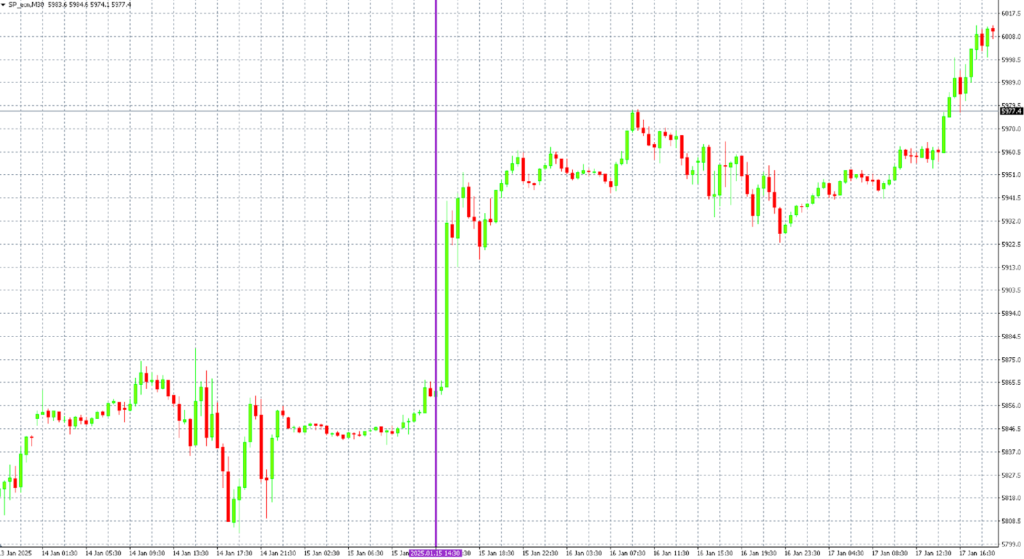
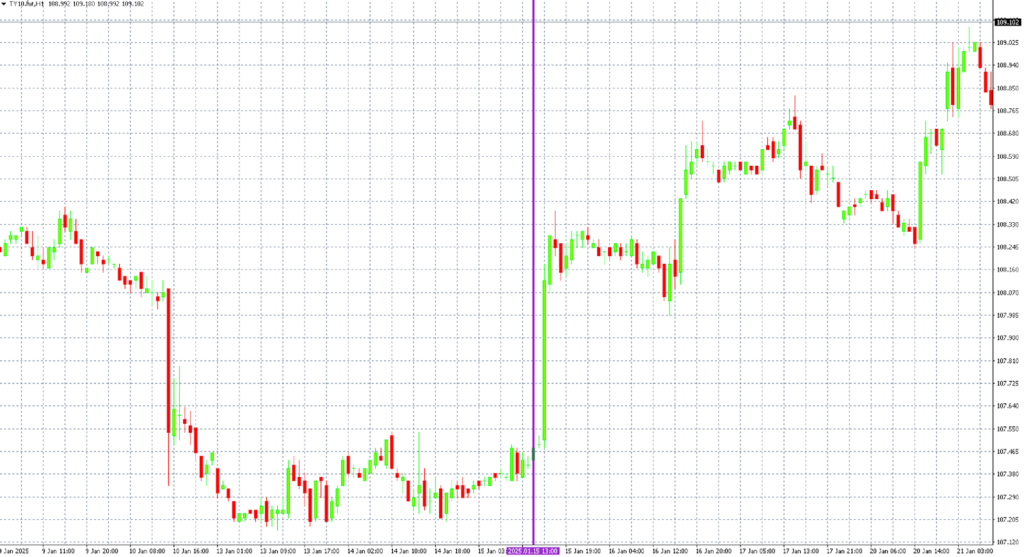
Inflation stats bring almost every fundamental trader to their screens each month. A surprise in either direction can cause massive volatility. Let’s take a look at the market reactions to the U.S. CPI announcement on January 15, 2025.
The December inflation report came at a time when the U.S. market was worried about stagnant inflation and tighter monetary policy, as reflected in the Fed’s December projections. Fed Chair Jerome Powell himself stated that inflation remains the key figure in the U.S. economy. This created the potential for significant market volatility.
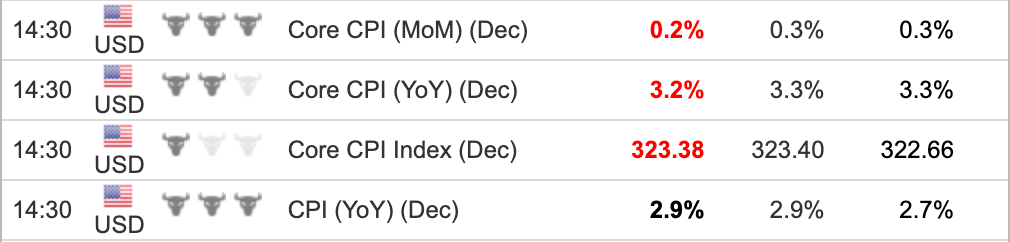
Markets expected headline CPI to accelerate to 2.9% and core CPI to 3.3% (expected figures shown in the middle). The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics ultimately reported headline inflation at 2.9%, while core inflation came in slightly lower at 3.2% and 0.2% month-over-month (actual figures on the left). Both figures exceeded expectations by 0.1%.
This triggered a sharp rise in U.S. stock indices, a brief weakening of the dollar, and a drop in 10-year bond yields accompanied by an increase in their price. However, reactions to inflation data are not always this pronounced – overall market sentiment also plays a crucial role.