Zoom In: Trading Fundamentals – The Labor Market and How to Trade It
If you want to trade news events successfully, you first need to understand them. That’s exactly what our fundamentals-focused section is here for. In part two of our series, we’ll show you how to read labor market data and, more importantly, how to use it to your advantage.

Fintokei is one of the few prop firms that allows trading during news announcements with no restrictions. So why not make the most of it? In our last episode, we explored how to trade inflation. Today, we’re zeroing in on how the unemployment rate, new job numbers, and other labor market indicators can move the markets. So let’s whip out our economic calendars and get to it!
Why Does the Labour Market Matter?
The labor market is a window into the broader economy. Strong job creation and rising wages often signal solid economic growth, potentially pushing inflation higher. In response, central banks might raise interest rates. On the flip side, weak employment data can indicate a slowing economy, increasing the likelihood of rate cuts.
Labor market data can cause sharp, rapid movements, especially in forex, stock indices, and bond markets. The US labor market, in particular, has a disproportionate impact globally. Yes, there’s a ton of data out there, but stick with us—by the end of this article, you’ll know exactly what to focus on.
Key Labour Market Indicators You Should Track
The US labour market is a data powerhouse, with reports released weekly, monthly, and quarterly. But not all numbers are equally important. Here are the ones that matter most:
Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate shows the percentage of people in the labour force who are jobless. A declining unemployment rate typically strengthens the USD, while a rising rate often weakens it. This crucial data point is released monthly—usually on the first Friday.
Average Hourly Earnings
Wage growth is a key driver of inflation. Rising wages can signal increasing inflationary pressure, pushing interest rates higher. Investors track both year-on-year and month-on-month changes, released alongside the unemployment rate.
Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP)
The most closely watched US jobs report. NFP data shows the number of new jobs created outside the agricultural sector. Strong numbers generally boost the dollar and stocks, while weak results can trigger market sell-offs. NFP is published monthly, together with the unemployment rate and earnings data.
ADP Nonfarm Payrolls
This private-sector report, released two days before the official NFP, often hints at the broader labor market trend. It can cause significant volatility despite occasional discrepancies with government data.
JOLTS (Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey)
This survey provides insight into job vacancies and the overall demand for labor. A high number of openings typically strengthens the USD. The data is published monthly, a few days before NFP.
Jobless Claims
This weekly report tracks the number of new unemployment benefit claims. It’s a leading indicator of labor market trends. While less impactful than monthly data, extreme deviations from forecasts can move markets.
What Markets Are Affected by Labor Market Data?
Labor market data can shake up multiple asset classes. The key markets to watch include:
USD (US Dollar)
A stronger labor market tends to strengthen the dollar, as it raises expectations for tighter monetary policy.
Gold (XAU/USD)
Gold often moves inversely to the dollar. Strong jobs data can weaken gold by driving interest rates higher.
US Stock Indices (S&P 500, Nasdaq, Dow Jones)
Stocks react differently depending on the context. A strong jobs report may boost equities if growth is moderate, but if inflation is a concern, stocks might drop.
Bond Yields (US10Y, US02Y)
Labour market strength can push yields higher, as investors anticipate rate hikes.
Trading Labour Market Data: Step-by-Step
Prepare Before the Release
- Check forecasts on sites like Investing.com.
- Analyze how similar reports have moved the market in the past.
- Identify the prevailing market sentiment. Is inflation a major concern? Are traders betting on a rate cut or hike?
React to the Data
Labor market releases often cause sharp market reactions within seconds. Here’s what typically happens:
- Better-than-expected data strengthens the domestic currency and may push stocks higher—unless inflation fears dominate.
- Worse-than-expected data usually weakens the currency and may trigger a stock sell-off.
Manage Your Risk
Volatility during labor market announcements can be extreme. Set stop-loss orders and avoid overleveraging your trades. Consider waiting for the initial volatility to subside before entering a position.
What Trading Labour Market Data Looks Like in Practice
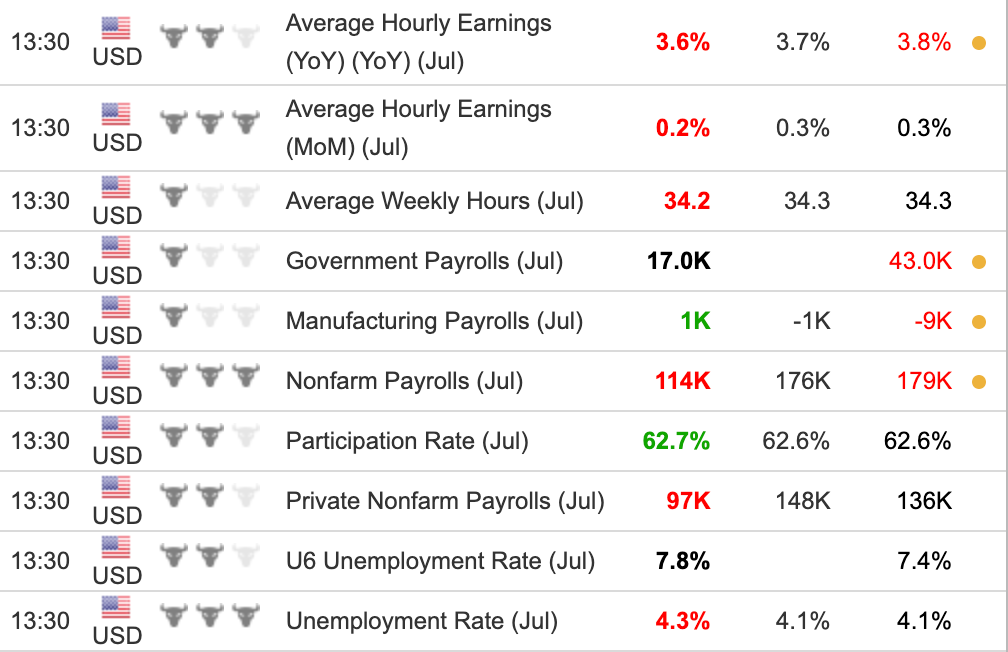
Let’s walk through a real-world example of how labor market data can impact the markets. We’ve chosen an extreme situation that unfolded following the release of the US labor market data on August 2, 2024.
To set the stage: at that time, the US was grappling with persistently high inflation. The Federal Reserve had been raising interest rates for months in an effort to curb these inflationary pressures. Ideally, the Fed hoped for a gradual weakening of the labor market to ease inflation, but what they got instead was a much sharper decline than expected.
The data release contained a lot of figures, but let’s zero in on the most significant ones: total unemployment, nonfarm payrolls (NFP), and average hourly earnings. All three metrics missed expectations:
- Hourly earnings fell more than forecasted.
- Nonfarm payrolls came in significantly below estimates.
- Total unemployment was well above the projected level.
At first glance, this sharp labor market weakening might seem like good news for the Fed’s inflation-fighting mission. But instead of celebrating, the market shifted its focus to fears of an impending recession.
Market Reactions
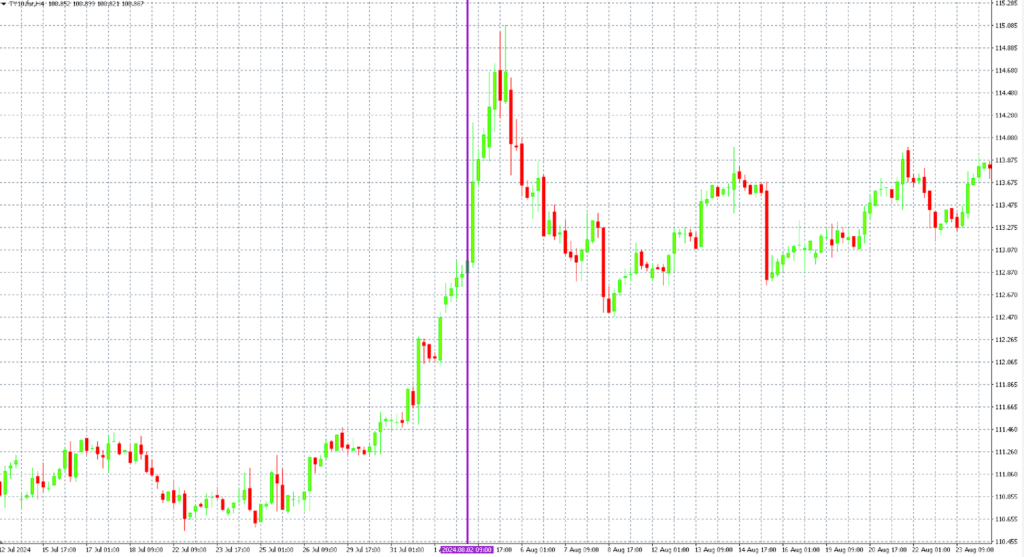
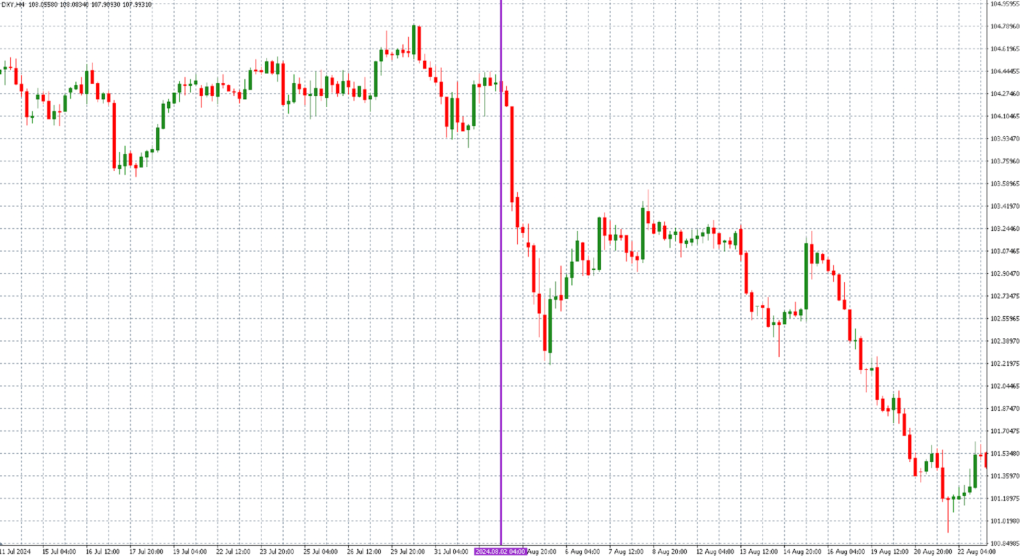
- US Dollar: The dollar weakened significantly across most currency pairs, driven by expectations of an imminent interest rate cut.
- Bond Market: The yield on the US 10-year Treasury bond plummeted, while its price surged—an indicator of growing concerns about economic growth.
- Equity Markets: Stocks also reacted strongly, with a notable correction following the release.
Key Takeaway
Labor market data can cause significant market moves, but context is crucial. In this case, the data revealed a weakening labor market, but instead of being bullish for stocks, it sparked recession fears that rippled across asset classes.
Trading these events successfully requires more than understanding the numbers—you need to grasp the broader market narrative as well.